Targeted RNAi Services
RNA interference (RNAi) is an evolutionarily conserved process that occurs in both humans and C. elegans to silence or inhibit specific genes by introducing double-stranded RNA (dsRNA) or small interfering RNA (siRNA). This technique involves multiple steps, such as the cutting of dsRNA, the formation of RISC, and the degradation of mRNA. RNAi is an important reverse genetic technology in C. elegans and has advantages like not changing genetic information, high efficiency, and good reproducibility compared to gene knockout methods.
How RNAi works in C. elegans
RNAi silences genes through post-transcriptional mechanisms. Key steps include:
1. dsRNA Processing: dsRNA complementary to the target mRNA is processed by Dicer into siRNAs (21–23 nucleotides).
2. RISC Formation: The siRNAs are incorporated into an RNA-induced silencing complex (RISC).
3. mRNA Degrading: RISC uses the siRNA to guide and degrade the target mRNA, silencing gene expression.
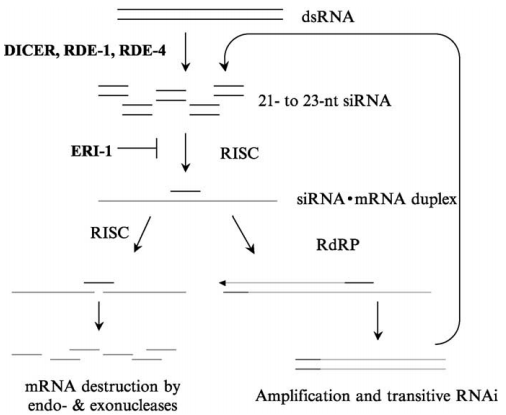
Figure 1. The molecular mechanism of RNA interference in Caenorhabditis elegans (Wang J , et al. , 2005.)
Our Services
RNAi services in C. elegans is a valuable tool for study gene function, explore disease mechanisms, and screen potential drug targets. Currently, there are four main RNAi methods tailored to your research needs:
ØRNAi by injection
1) Directly inject in vitro synthesized dsRNA into young adults.
2) Reliable for individual gene knockdown but more time consuming and labor intensive than other methods.
ØRNAi by soaking
1) Immerse C. elegans in a dsRNA solution.
2) Suitable for moderate-scale experiments or high-throughput screenings.
3) Applicable to all developmental stages.
ØRNAi by feeding
1) Deliver dsRNA to C. elegans via bacteria expressing the dsRNA.
2) Cost-effective and labor-saving.
3) Supports large-scale studies, though results may vary slightly.
4) Applicable to all developmental stages.
ØTransgenic RNA interference
1) Generate dsRNA hairpins using inverted repeat (IR) plasmids.
2) A constitutive (such as heat shock) or tissue-specific promoter for precise gene silencing, and the plasmid(s) is injected into C. elegans to construct a transgenic nematode strain.
3) Suitable for creating specialized transgenic strains.
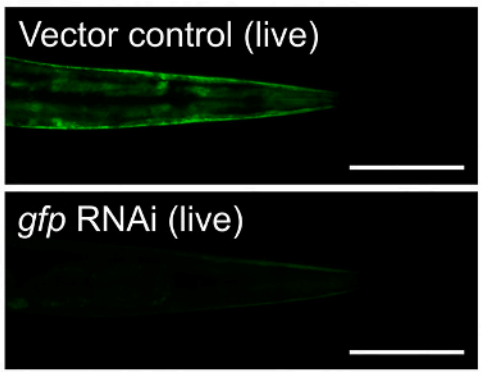
Figure 2. Feeding RNA interference inhibits gfp expression (Baumanns S., et al ., 2022)
References
1. Wang J , Barr M. RNA Interference in Caenorhabditis elegans [J]. Methods in Enzymology, 2005, 392(Chapter 26):36-55. doi : 10.1385/1-59259-935-4:029.
2. Baumanns S, Beis DM, Wenzel U. RNA-interference in the nematode Caenorhabditis elegans is effective using paraformaldehyde-inactivated E. coli HT115 bacteria as a food source. Biochim Biophys Acta Mol Cell Res. 2023 Jan ;1870 (1):119375. doi : 10.1016/j.bbamcr.2022.119375.


