How C. elegans Is Used in Tumor/Cancer Research
C. elegans, a small nematode worm, has been widely used in cancer research due to its genetic tractability, transparency, and conserved molecular pathways. Although C. elegans itself does not develop cancer, many fundamental processes underlying cancer—such as cell proliferation, apoptosis, and signaling pathways—are highly conserved between C. elegans and humans. This allows researchers to use C. elegans as a model system to study key aspects of tumorigenesis.
Key Reasons C. elegans Is Used in Tumor/Cancer Research:
· Genetic Conservation: Around 65% of human disease genes, including many involved in cancer, have orthologs in C. elegans.
· Drug Screening: C. elegans is used to screen chemotherapeutic agents and identify new compounds that can inhibit cancer pathways.
· Rapid Life Cycle: Their short life span allows for high-throughput genetic screens to identify genes involved in cancer processes.
· Transparency: The transparency of C. elegans allows real-time observation of cellular processes like cell division and apoptosis in vivo.
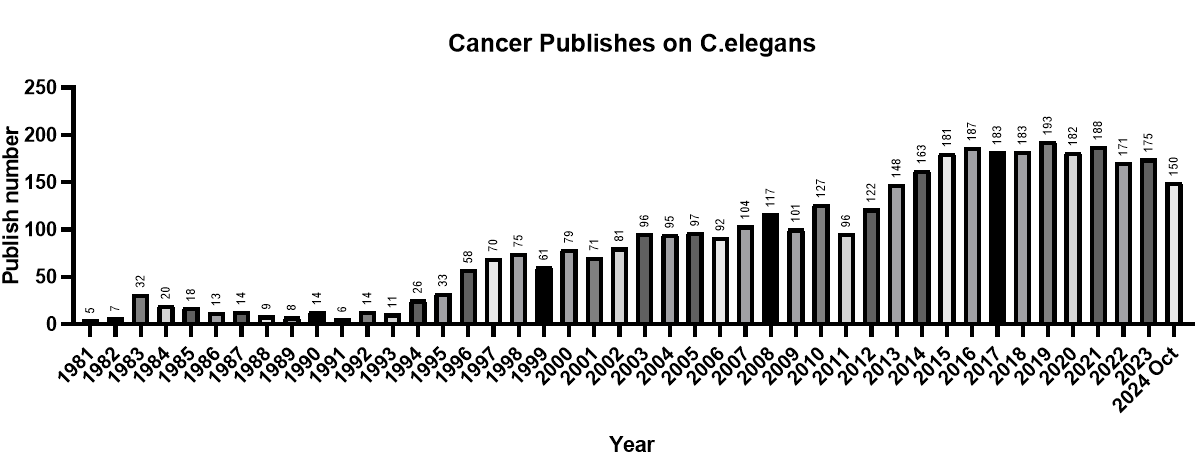
Over the past 45 years, interest in using C. elegans for cancer research has grown significantly. A search on PubMed shows that more than 3,876 papers were published between 1980 and 2024 investigating cancer-related processes in C. elegans. These studies have shed light on a wide variety of cancer-relevant mechanisms, including cell cycle regulation, apoptosis, and signaling pathways such as Ras and Wnt.
Common/Conserved Tumor/Cancer Pathways Found in C. elegans
Several key cancer-related pathways in humans are conserved in C. elegans, making it a valuable model for studying tumorigenesis. Below is a table comparing some common cancer-related genes between humans and C. elegans:
Human Gene | Pathway | Function | Conservation | C. elegans Ortholog | Role in C. elegans |
RAS | Ras/MAPK | Oncogene, cell growth | YES | let-60 | Vulval development |
TP53 | p53 | Tumor suppressor, DNA repair | YES | cep-1 | Apoptosis, DNA repair |
PI3K | PI3K/Akt | Cell growth, survival | YES | age-1 | Longevity, stress resistance |
WNT | Wnt | Cell fate determination, migration | YES | lin-44, egl-20 | Cell polarity, migration |
BRCA1 | DNA Damage Response | DNA repair, tumor suppressor | YES | brc-1 | DNA damage response |
PTEN | PI3K/Akt | Tumor suppressor, cell cycle arrest | YES | daf-18 | Regulation of dauer formation, cell survival |
EGFR | Ras/MAPK | Epidermal growth factor signaling | YES | let-23 | Vulval induction, cell proliferation |
MYC | Ras/MAPK, PI3K/Akt | Transcription factor, cell cycle | YES | mdt-1 | Cell proliferation |
Notch | Notch | Cell differentiation, apoptosis | YES | glp-1 | Germline stem cell maintenance |
SMAD | TGF-β/SMAD | TGF-beta signaling, cell differentiation | YES | sma-2, sma-3 | Body size regulation, cell signaling |
Accelerate Your Cancer Research: Comprehensive Genotypic and Phenotypic Services Tailored to Enhance Your Research
Genotypic Services | Description |
Efficient gene editing tailored specifically for C. elegans using CRISPR/Cas9. (Hyperlink to reach the service detail). | |
Create extrachromosomal arrays and integrate them into the genome of C. elegans. (Hyperlink to reach the service detail). | |
Insert single-copy transgenes into the C. elegans genome for stable expression. (Hyperlink to reach the service detail). |
Phenotypic Services | Description |
EMS Screen for Tumor Genes | Mutagenesis to identify new tumor suppressors or oncogenes in cancer pathways. |
Tumor Phenotype Collection | Collection of genetically engineered C. elegans lines with cancer-like traits. |
Drug or Compound Screening | High-throughput drug testing for anticancer activity using tumor models. |
RNAi Screening for Tumor Genes | RNAi screens to discover tumor suppressors, oncogenes, or drug targets. |
Apoptosis, Proliferation, Metastasis Assays | Phenotypic assays for assessing key cancer traits in C. elegans. |


